Action Flow
Action flow is the ability to execute multiple actions in succession.
It also has an action chain function that passes the return value of one action to another.
Usage scenarios
Action flows are called from the following functions
- When a trigger is fired
- When an action is immediately executed
- During scenario execution
Actions
The following types of actions are available. It is also possible to add custom actions using filter hooks.
- Actions that retrieve and return information
- Actions that search for information and return it
- Actions that perform operations such as sending messages
Actions are shared with the Function Calling feature used for AI responses.
Return Value of Actions
Send the return value as a response
If checked, the action's return value will be sent as a LINE message to the event source.
The event source is the event sender user if the trigger type is a Webhook event; otherwise, it is the user specified in the audience.
The type of message sent varies depending on the type of return value:
- String: Sent as a LINE text message
- Instance of LINE\LINEBot\MessageBuilder: Sent as a LINE message object
- Others: Sent as a dumped LINE text message
Embedding Variables
If the argument of the action is a string, each variable can be embedded and used.
The following variables are available:
Return Values of Actions
The return values of sequentially executed actions can be used in placeholders within the arguments of subsequent actions.
{{ return[action_number] }}
action_number is the order of actions starting from 1.
If the return value of the target action is an array, you can extract a specific value by adding ".key" after the action number in parentheses.
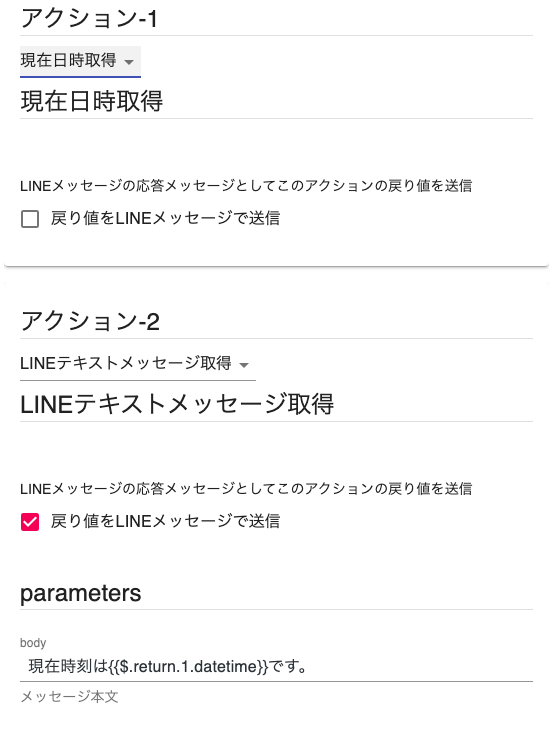
Example: Set the "Get Current Date and Time" action to Action-1 (Action Number 1).
Set the "Get LINE Text Message" action to Action-2 (Action Number 2).
In the body of the parameters for Action-2, enter "The current time is {{ return[1].datetime }}."
This will embed the current time in the message and send it.
Webhook Event Data
You can also use data included in received Webhook events.
{{ webhook.eventObjectProperty }}
Example: To use the text message sent to the official account
{{ webhook.message.text }}
Example) When using postback data
You can use the data directly with {{ webhook.postback.data }}.
When data is in query string format, the parsed data is stored in params.
Example) Replying with a specified message ID using postback
If the data is action=message&slc_message_id=1354, you can use {{ webhook.postback.params.slc_message_id }} to get the value "1354".
By utilizing this, you can create a single common trigger that fires on action=message, set the "Get LINE Connect message" action, and inject the desired message ID through action chain. This eliminates the need to create individual triggers for each message.
Configuration Example
Example) Setting profile items using postback
Create a postback with data action=profile&key=value and configure the trigger to fire on action=profile.
Select "Update LINE User Profile" as the action and input {{ webhook.postback.params.key }} for key and {{ webhook.postback.params.value }} for value.
Configuration Example
User Data
You can use the data of the user who sent the Webhook event.
{{ user.WPUser object properties }}
Example: Using the display name of a user
If the user is already linked to a WordPress user, you can get the display name of the WordPress user; if not, you can get the display name of the LINE user.
{{ user.data.display_name }}
The profile of the LINE user (profile image URL, etc.) can be used in {{ user.profile.profileProperty }}.
The standard available values for profile properties are displayName, pictureUrl, language, and statusMessage.
In addition, you can use your own item names set in the profile update action.
Action Chain
If the argument of an action is in the form of an object or a predetermined constant to be selected from, embedding variables is not possible.
In such cases, a chain rule can be added to inject the return value of any action into the arguments of subsequent actions.
Destination argument
How to Specify the Target Action Argument for Injection: ActionNumber.ArgumentName
- Action Number: The order of the actions starting from 1
- Argument Name: The name corresponding to the required argument for each action
Example: To specify the message of action-2 as the injected argument:2.message.
(Note that it is not necessary to enclose in{{ }}and dot notation is used instead of bracket notation)
Data
Data to be injected can be strings or embedded variables as mentioned above.
Injecting objects directly
To inject objects directly rather than as strings, add a $. to the beginning of the specification.
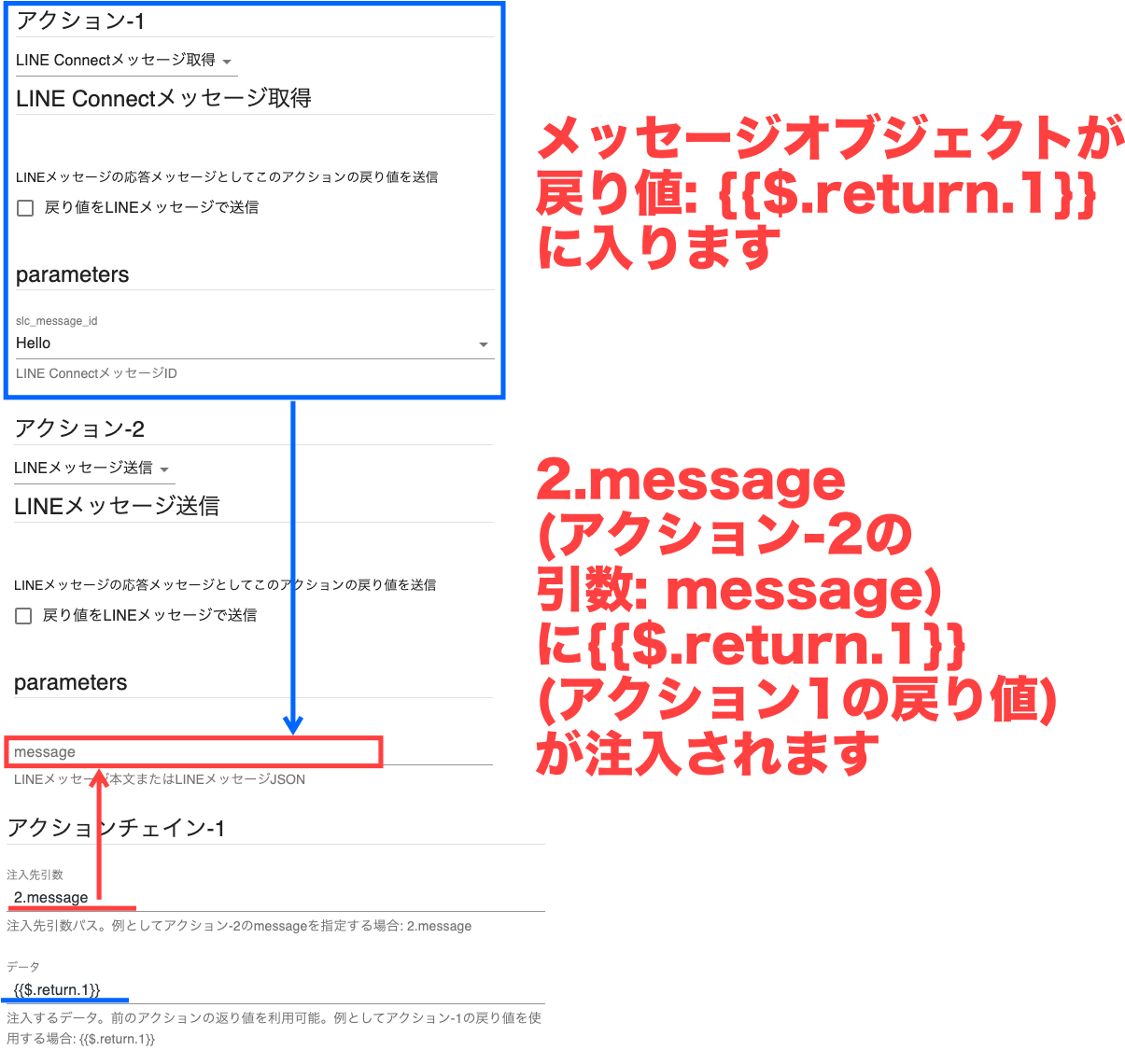
Example: Create an action flow where Action 1 retrieves a LINE Connect message and Action 2 sends a LINE message.
In this case, you need to pass the LINE message object from Action 1's return value as an object to Action 2.
Set the destination argument to 2.message and the data to inject as {{ $.return[1] }}.
Template Engine
The embedding of variables using placeholders is executed using the Twig template engine. You can use Twig's tags, functions, and filters to perform complex operations such as conditional branching and loop processing. For more information about Twig, refer to the Twig Official Documentation.
Conditions for using Twig
- PHP 8.1 or higher
Conditions for not using Twig
- When the placeholder contains only one variable and the variable starts with $. (Since Twig cannot output objects, when injecting objects, the processing is performed internally by LINE Connect rather than Twig)